More about the project
Concept and activities
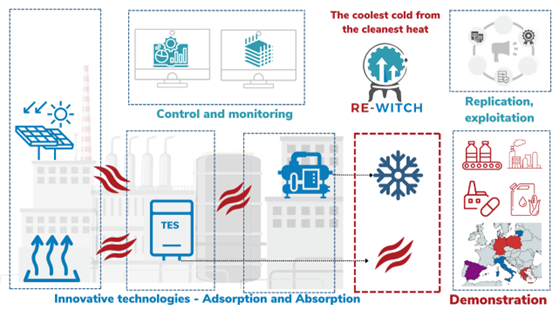
RE-WITCH aims at developing and demonstrating innovative efficient thermally-driven cooling and heating technologies for industrial processes, game-changers solutions to unlock the potential of low-grade waste and renewable heat use in industries. Innovative open access modelling platforms and engineering solutions will be also developed to facilitate the design, upscale, replication and integration of the proposed technologies in industrial processes.
RE-WITCH will:
- Develop and demonstrate innovative thermally-driven technologies, based on i) a new generation of ADsorption chillers, more compact and less expensive, to be either directly integrated in the process or provided in a containerized solution along with air compressors and ii) 2 new working cycles of ABsorption chillers, integrating a mechanical compressor providing both heating and cooling as well as a dual evaporator/absorber providing cooling at different temperature levels and thermal powers.
- Foresee an optimised techno-economic integration between low-grade (<100 °C) industrial waste heat and high-efficiency vacuum flat plate solar collectors, to drive process cooling generation and provide process heating.
- Demonstrate the innovative Ad/Absorption cooling solutions in 4 demo sites, covering typical industrial sectors with high cooling demand (food and beverage) and non-standard sectors (biofuels production). Complementing the demonstration with 3 replication sites, covering other possible relevant sectors (pulp and paper, DHN-connected industries, data centers), investigating RE-WITCH potential applications and benefits.
Objectives
- Integration of renewable heat or industrial waste heat in heat-to-cold conversion systems to generate cold for industrial processes, with targets to advance the technologies readiness level in terms of capacity and temperature,
- Valorisation of low-grade waste heat and high-efficiency renewable sources for the future industrial cooling provision,
- Identify the target industrial processes, assess the impacts on these processes in terms of energy savings and GHG and air pollutant emissions reductions. Preliminary assessment at proposal stage,
- Improve the refrigeration system efficiency and environmental friendliness: controls, innovative materials, components, working fluids,
- Integrate and demonstrate the refrigeration system in an industrial application in at least one industrial sector,
- Identify the potential technical and non-technical barriers, investigating notably other mitigation alternatives than gas-fired backups,
- Analysis of the potential industrial applications and related benefits (technical, economic, climatic, environmental), and the integration of RE-WITCH innovations in the overall network,
- Define an exploitation strategy, including a strong business case and sound exploitation strategy, toward the technologies’ commercialization, to plan future commercial demonstrations supported, for instance, by the Innovation Fund as well as to drive new policy recommendations to support:
- the deep decarbonization of industrial sectors,
- increase of the competitiveness of EU industry for process H&C,
- reduction of fuel dependency.
Work plan
- WP4 – Process requirements and industrial sectors mapping toward RE-WITCH technology design and integration (UoB)
- WP5 RE-WITCH System simulation and modelling approach for technology design, demonstration and replication (UNIGE)
- WP6 Innovative adsorption technology design (Sorption Technologies)
- WP7 Innovative absorption technology design (BS NOVA)
- WP8 Innovative cooling technologies manufacturing and testing (CNR)
- WP9 System integration and demo sites design (IDP)
- WP10 Final implementation including systems integration and procurement (IDP)
- WP11 Monitoring platform and control development (SIGLA)
- WP12-13 Demo sites pre-monitoring and installation + Demonstration campaign at TRL7 (TECNALIA)
- WP14 -16 Business modelling, standardization and exploitation (IVL)
- WP 17 Economic, environmental and replication analysis (PNO)
- WP18-20 Stakeholder oriented dissemination and communication activities (IEECP)
Demo cases
RE-WITCH will demonstrate its innovative Ad/Absorption cooling solutions in 4 demo sites, covering typical industrial sectors with high cooling demand (food and beverage: BROWAR in Poland and COVAP in Spain) and non-standard sectors (biofuels production: MILOIL in Greece).
FOCUS ON… COVAP – SPAIN
- Simultaneous Heating & Cooling for the food industry.
- Plant in Pozoblanco.
- Technologies demonstrated: Hybrid absorption/compression Heat Pump (100kWc/250kWh)) and solar thermal (80-100m²).
- Technology providers: BS-NOVA and TVP Solar.
FOCUS ON… MILOIL – GREECE
- Cooling at different temperature levels.
- Technologies demonstrated: dual evaporator/absorber chiller (40kW (10°C) & 400kW (20/25°C) and solar thermal (30kW).
- Technology providers: BS-NOVA and TVP Solar.
FOCUS ON… BROWAR Głubczyce – POLAND
- A low temperature cooling installed in a brewery.
- Technologies demonstrated: Adsorption chiller (200kW) and solar thermal (50-70kW).
- Technology providers: SOR and TVP Solar.
Focus on... the technologies
Briefings presenting each technology are under preparation.
RE-WITCH will develop and test:
- A new generation of ADsorption chillers, more compact and less expensive, to be either directly integrated in the process or provided in a containerized solution along with air compressors.
- 2 new working cycles of ABsorption chillers, integrating a mechanical compressor providing both heating and cooling as well as a dual evaporator/absorber providing cooling at different temperature levels and thermal powers.
Absorption cooling is a technology exploiting the ability of a liquid solution, based on a sorbent (e.g. LiBr) and a refrigerant (e.g. water), to perform a refrigeration cycle driven by low-grade waste/RES, thus substituting a mechanical compressor. It is considered as SoA technology, however, all sorption cooling devices are bound to hard restrictions concerning temperatures: driving heat temperature and chilling temperature set limitations to the reject heat temperature which can be attained. Technologies developed and demonstrated during RE-WITCH can overcome these limitations, by breaking the tight link between the thermodynamic states of the different components which provide cooling at low temperature T0, output of heat at medium temperature T1, and consume driving heat at high temperature T2. These limitations arise from the equilibrium data of the working fluid pair LiBr/water and the crystallization of the mixture at low water content.
Two different approaches are proposed to accomplish flexible use of sorption heat pumps for heat upgrade and cooling in various industrial constellations: i) single-stage sorption heat pump cycle complemented by a mechanical vapor compressor in order to achieve an increased temperature lift for simultaneous H&C; ii) evaporator-absorber pair duplicated in order to provide cooling at different temperature levels increasing the flexibility also thanks to an innovative control approach.
- An optimised techno-economic integration between low-grade (<100 °C) industrial waste heat and high-efficiency vacuum flat plate solar collectors, to drive process cooling generation and provide process heating.
RE-WITCH will implement a Digital Twin (DT) platform for district heating (DHN) for RE-WITCH solutions, BIM-based engineering of RE-WITCH solution integration as well as develop an innovative integrated control and monitoring platform and use Open access (OA) numerical modelling and optimization platform.
Knowledge sharing
REPORTS
Please note that the project reports will be added as they are published, along the project life and that the following publications are still subject to the European Commission’s approval.
- D4.1 – First release of industrial cooling needs and RE-WITCH technology specifications, M12
- D4.3 – Key performance indicators for RE-WITCH evaluation and RE-WITCH Academy material prepared, M15
- D14.1 – Analysis of related EU, national and/or regional policies, and standards, M16
- D16.1 – Final checklist of alignment of the solutions with standards and policy recommendations at national and EU level, including BREF, M47
- D17.1 – Replication feasibility studies and assessment of potential integration of REWITCH technologies in different industrial environments and DHNs also considering TES integration, M48
- D17.2 – Economic, environmental and social impact assessment of RE-WITCH technologies, M48
Other project reports are planned to be confidential, yet, partners will strive to make results available in shorter format such as briefings, infographics, and more.
Communication and administration reports
MULTIMEDIA
Videos, factsheets, briefings and graphics will be added in this section, stay tuned!
Useful resources and projects
PROJECTS
Contact
The project is coordinated by CNR – Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche: Andrea Frazzica – andrea.frazzica(a)cnr.it
For communication or media related questions, please contact Marine Perrio, IEECP – marine(a)ieecp.org